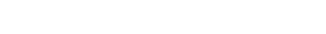
The best choice for a healthy life
What is PDT HOME > PDT/PDD > What is PDT
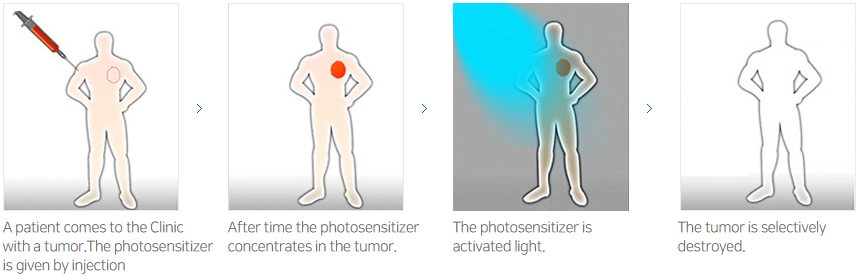
Photodynamic Therapy
A new cancer treatment method using rich amount of oxygen in the body, laser supplied from outside, and photosensitizing agent that is sensitive to laser light.
About PDT
PDT (Photodynamic Therapy) is a new cancer treatment method using high amount of oxygen in the body, laser supplied from outside, and photosensitizing agent that is sensitive to laser light. When the photosensitizer is injected intravenously, tumor tissue cells and tumor vascular tissues are selectively accumulated. After a certain period of time, the single wavelength of laser light that can only be absorbed by the photosensitizer material, make photo-sensible material in excitation state. This energy is then transferred to oxygen molecules in the tumor tissue to produce active oxygen species (single antigen, oxygen radical, superoxide and peroxide) and direct absorption of the tumor to necrotize it. Also, only tumor tissue is selectively necrotized in a complex way according to the secondary reaction such as apoptosis and induced immunological response, that occurred from oxidative stress.
Advantages of PDT
- Tumor Specific Therapy
- Treatment of various cancers such as lung, stomach, esophagus, uterus, bladder, skin cancer, etc.
- Substitution of surgery (cancer patients who cannot perform surgery, patients who hate surgery, and the elderly with weak physical strength)
- Repeated treatments can be performed at a time without side effects depending on the condition of the palliation cancer
- Preservation of the function of the organs that can be preserved during treatment (ex. Vocal cords, uterus, anus) that has a failure during surgery
- Can be combined with other cancer treatments
- The treatment of recurrent cancer
Process of PDF Treatment
History of PDT
History of PDT (Photodynamic Therapy) begins in 1898, when Oscar Raab, a medical student in Munich, Germany, discovered that a paramecium aurelia stained with acridine red was exposed to light and died. Then in 1904, he realized that oxygen is necessary through phosensitive response, and was the first to use term “photodynamic action”, according to his professor Von Tapeiner. In 1978, the first trial was attempted by Thomas Dougherty to patients with skin malignant tumor, who did not show any responses to prior treatments. PDT treatment was first studied in 1980s and have been approved in Canada, Germany, and Japan in the 1990s.
Also, pre-clinical and clinical problems have mostly been clarified thanks to the active exchanges and cooperation between subjects, and the wide-area of dynamic treatments have also been evaluated in many areas as a new clinical and diagnostic method. In addition, the FDA granted permission of Porfimer Sodium to treat esophageal cancer in January 1996, and approved early lung cancer treatment in September, 1997.
Mechanisms of PDT
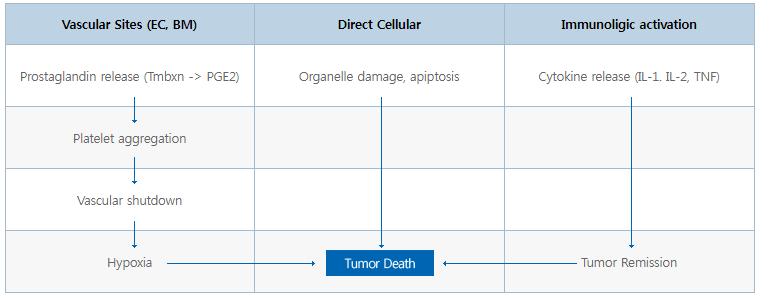
In general, the three essential elements of PDT use light sources, photo-sensitive materials, and oxygen. By investigating the proper wavelength and proper amount of light and activate photo-sensitive material, it either acts directly or creates reactive oxygen to the target cell.
Photosensitizer Excitation in tumor tissue Release of active species


